Understanding Brain Surgery Tools: Unveiling the Essentials for Successful Procedures
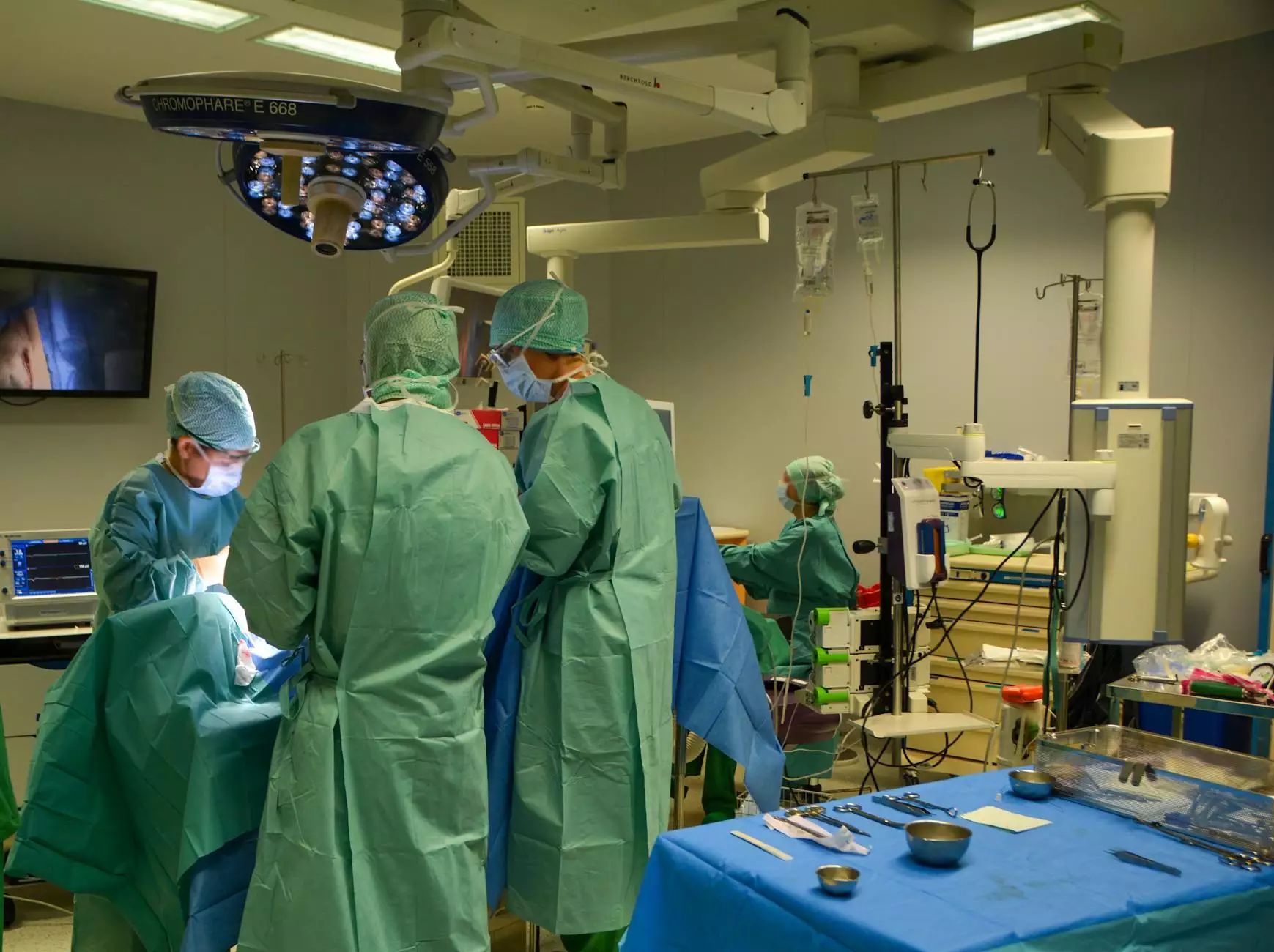
In the field of neurosurgery, the precision and efficiency of procedures rely heavily on the quality and design of the tools used. Among these, brain surgery tools stand out due to their critical role in ensuring successful outcomes. This article will delve deeply into the various categories, applications, and innovations in brain surgery tools, highlighting their importance in health and medical practices.
The Importance of Brain Surgery Tools
The human brain is a complex and delicate organ that requires the utmost care during surgical interventions. The use of specialized brain surgery tools enhances the surgeon's ability to operate effectively while minimizing risks. As medical technology advances, the tools for neurosurgery continue to evolve, offering greater precision, safety, and effectiveness.
Categories of Brain Surgery Tools
Brain surgery tools can be categorized into several distinct types, each serving specific purposes:
- Scalpels: Used for incising skin and tissue.
- Scissors: Surgical scissors designed for precision in tissue cutting.
- Forceps: Instruments for grasping and holding tissues.
- Electrocautery devices: Utilized for cutting and coagulating tissue using electrical currents.
- Suction devices: Essential for removing fluids, blood, and debris.
- Retractors: Instruments to hold back tissues to give the surgeon clear access to the surgical site.
- Neurosurgical drills: Used for opening the skull and accessing the brain.
- Endoscopes: Allow for minimally invasive procedures through small incisions.
Key Brain Surgery Tools and Their Uses
1. Scalpels
Scalpels are among the most fundamental brain surgery tools. They come in various shapes and sizes, suited for different types of incisions. The precision of a scalpel allows neurosurgeons to make clean cuts, minimizing trauma to surrounding tissues.
2. Surgical Scissors
Designed specifically for surgical purposes, these scissors can cut through delicate brain tissue and other structures with ease. There are various specialized types, including:
- Metzenbaum scissors: Ideal for cutting delicate tissues.
- Mayo scissors: Suitable for cutting thicker tissues.
3. Forceps
Surgical forceps are critical for grasping tissues during procedures. They come in various designs, including:
- Debakey forceps: Used for delicate tissues.
- Allis forceps: Ideal for holding and manipulating tissues securely.
4. Electrocautery Devices
These advanced tools use electric currents to cut through tissue and simultaneously coagulate blood vessels, reducing bleeding during surgery. Their use is pivotal in neurosurgical procedures, where blood loss can complicate operations.
5. Suction Devices
Fluid management is crucial during brain surgery to maintain a clear surgical field. Suction devices effectively eliminate blood and cerebrospinal fluid, enabling surgeons to see clearly while operating.
6. Retractors
Retractors are invaluable in keeping incisions open, allowing for better visibility and access. Various retractors are available, including:
- Self-retaining retractors: Hold themselves in place, freeing the surgeon's hands.
- Hand-held retractors: Require assistance from an assistant or the surgeon to maintain position.
7. Neurosurgical Drills
These powerful tools enable surgeons to create openings in the skull (craniotomy) with precision. The drill's advanced technology allows for controlled depth and speed, reducing the risk of damaging brain tissue.
8. Endoscopes
Endoscopic tools have transformed neurosurgery by enabling minimally invasive approaches. These instruments are equipped with cameras, allowing surgeons to visualize the brain through small incisions, leading to quicker recovery times for patients.
Innovations in Brain Surgery Tools
The medical industry is continuously evolving, and so are the brain surgery tools. Innovations are enhancing the capabilities of these tools, leading to improved outcomes and safety in procedures. Here are some notable advancements:
Robotic-Assisted Surgery
Robotic systems are beginning to play a significant role in neurosurgery, offering unparalleled precision. Surgeons can control robotic arms equipped with surgical tools, allowing for more intricate maneuvers and greater control over delicate operations.
3D Printing of Surgical Instruments
3D printing technology has made it possible to create customized surgical tools tailored for specific procedures and even for individual patients. This can significantly enhance the effectiveness of surgeries and improve surgical outcomes.
Smart Surgery Tools
With the advancement of artificial intelligence and machine learning, smart surgical tools are being developed that provide real-time data and feedback to surgeons. These tools can enhance decision-making and increase safety during operations.
The Future of Brain Surgery Tools
As technology continues to advance, the future of brain surgery tools looks promising. Innovations such as augmented reality and enhanced imaging technologies will likely become increasingly integrated into surgical practices. This integration will provide neurosurgeons with augmented capabilities to visualize the brain in ways that were previously unimaginable.
Caring for Instruments
To maintain the efficiency and longevity of brain surgery tools, proper care and sterilization practices are essential. These tools must be meticulously cleaned, disinfected, and inspected regularly to ensure safety and compliance with medical standards.
- Cleaning: Rinse instruments immediately after use to remove organic matter.
- Sterilization: Use autoclaving or other approved methods to sterilize surgical tools.
- Inspection: Regularly check for wear and damage to ensure all tools function correctly.
Conclusion
The realm of brain surgery is intricate, demanding not only exceptional skill but also the best tools available. The right brain surgery tools can make a significant difference in the success of surgical procedures and the well-being of patients. Understanding these instruments, their functions, and the advancements in technology can help medical professionals make informed decisions and ultimately improve patient outcomes.
As we continue to innovate and improve within the field of health and medical supplies, the future of neurosurgery appears bright. With continuously evolving technology, we are on the verge of achieving groundbreaking advancements that will redefine surgical capabilities and enhance the surgical experience for both surgeons and patients alike.









